Buy LL-37 CAP-18 Peptide
Buy LL-37 CAP-18, a human antimicrobial peptide belonging to the cathelicidin family, known for its role in the immune response by combating infections, promoting wound healing, and modulating inflammation.Shop our Full Range of LL-37 (CAP-18) Peptides
-

LL-37 Peptide Vial
£38.84 – £47.82Price range: £38.84 through £47.82 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

LL-37 Nasal Spray
£45.84 – £86.68Price range: £45.84 through £86.68 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

LL-37 (Cap-18) Pre-Mixed Pen 5mg
£45.25 – £122.18Price range: £45.25 through £122.18 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

Thymosin Alpha-1 LL-37 VIP Peptide Stack
£111.88Original price was: £111.88.£100.69Current price is: £100.69. -
Sale!

Thymosin Alpha-1 LL-37 Nasal Stack
£99.08 – £189.16Price range: £99.08 through £189.16 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

LL-37 Thymosin Alpha-1 Peptide
£85.58 – £94.56Price range: £85.58 through £94.56 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
What Is LL-37 (CAP-18)?
LL-37, also known as CAP-18, is a naturally occurring helical peptide. It consists of 37 amino acids that play a vital role in host defense mechanisms. It is the only cathelicidin identified in humans and is primarily produced by white blood cells, epithelial cells, and keratinocytes.
This peptide is crucial for protecting the body by directly killing bacteria, viruses, and fungi, thereby preventing bacterial invasion and infections. Beyond its antimicrobial properties, LL-37 is involved in regulating cytokine expression, which signals the immune system to respond effectively to infections and injuries. Additionally, it influences neutrophil apoptosis, ensuring a balanced immune response.
LL-37 also supports wound healing by promoting cell growth and tissue repair while modulating inflammation to prevent excessive immune reactions. Its unique functions, including its role in extending the life span of host cells and maintaining the body’s first line of defense, make LL-37 an indispensable component of the immune system.
LL-37 (CAP-18) Mechanism Of Action
LL-37 (CAP-18) works by directly and indirectly protecting the body from infections and managing immune responses. It attacks harmful microorganisms by binding to their membranes and inserting itself into the lipid layers. This creates pores, destabilizes the membrane, and ultimately kills bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
It not only fights microbes but also helps regulate the immune system. It plays a key role in attracting and activating immune cells like neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells by interacting with their receptors. It also supports infection clearance by triggering the release of chemokines and cytokines, which coordinate the immune response. Importantly, LL-37 helps control inflammation, preventing the immune system from overreacting and causing tissue damage.
These mechanisms make LL-37 a versatile and essential tool in both fighting infections and maintaining immune balance. This highlights its value in therapeutic research and potential clinical applications.
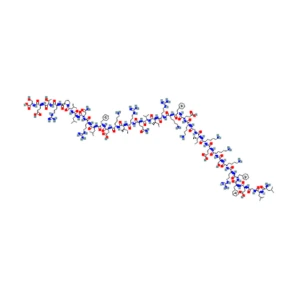
Structure of LL-37 (CAP-18)
Sequence: H-Leu-Leu-Gly-Asp-Phe-Phe-Arg-Lys-Ser-Lys-Glu-Lys-Ile-Gly-Lys-Glu-Phe-Lys-Arg-Ile-Val-Gln-Arg-Ile-Lys-Asp-Phe-Leu-Arg-Asn-Leu-Val-Pro-Arg-Thr-Glu-Ser-OH
Molecular Formula: C205H340N60O53
Molecular Weight: 4493 g/mol
PubChem CID: 16198951
What Are The Research Benefits of LL-37 (CAP-18)
Managing Inflammation: Studies show it is involved in inflammatory diseases like psoriasis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis [1]. Research has demonstrated its effects vary depending on the inflammatory environment, influencing immune responses such as keratinocyte apoptosis, IFN-alpha production, chemotaxis, and cytokine regulation. It appears to balance the immune system, reducing overactivity during infections and potentially regulating autoimmune inflammation. While previously thought to worsen autoimmune diseases, recent evidence suggests it may actually help prevent excessive inflammation in these conditions [2].
Arthritis Management: Research suggests that its a peptide found in high concentrations in joints with rheumatoid arthritis. However, it is likely beneficial rather than causative in inflammation. Evidence indicates that LL-37 deficiency does not worsen outcomes in arthritis or lupus, leading scientists to believe its presence is a response to inflammation rather than a trigger [3].
Studies in mouse models reveal that LL-37-derived peptides can protect against collagen damage and reduce disease severity [4]. Additionally, it may help regulate inflammation caused by interleukin-32 and interact with toll-like receptor pathways to potentially reduce inflammatory responses, though further research is needed [5].
Antimicrobial Properties: It exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, targeting bacteria, viruses, and fungi to prevent and combat infections. As part of the innate immune system, it is activated during infections and accumulates in response to pathogens [6].
Studies have shown it binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), disrupting the membrane of gram-negative bacteria, while also demonstrating potent effects against gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Additionally, it enhances the activity of lysozyme, making it a vital component of host defense. Research continues to explore its potential as a treatment for serious bacterial infections [7].
Biofilm Disruption: It has shown significant potential in disrupting biofilms, which are structured communities of microorganisms encased in a protective matrix. Biofilms are notoriously resistant to antibiotics and the immune system, often contributing to chronic infections. It can penetrate these protective barriers, breaking down the biofilm structure and exposing the embedded pathogens to immune cells and antimicrobial agents. This ability highlights its role as a crucial factor in combating biofilm-associated infections and promoting effective treatment strategies [8].
Role in Sepsis: The peptide plays a vital role in the body’s defense against sepsis, a life-threatening condition triggered by an overwhelming immune response to infection. It helps by neutralising bacterial toxins, reducing excessive inflammation, and enhancing the immune system’s ability to combat pathogens. These antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties make it a potential therapeutic target in managing sepsis and improving patient outcomes [9].
Respiratory Issues: It has been studied for its potential role in treating lung diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce lung infections and inflammation, which are common in these conditions [10].
Research suggests that it plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses within the lungs, preventing excessive inflammation while combating harmful pathogens such as bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [11].
Additionally, the peptide supports lung healing by attracting epithelial cells to injury sites, aiding wound closure, and promoting blood vessel growth. This peptide shows promise as a therapeutic candidate for respiratory illnesses, helping maintain airway and immune system balance [9].
Intestinal Health: Studies show that it may support intestinal health by helping cells migrate to maintain the epithelial barrier. This can help in reducing inflammation-related cell death, and potentially aid in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease or acute infections. It could also work alongside antibiotics to reduce gastrointestinal side effects [12].
Research also indicates that it works with human beta defensin 2 to promote wound healing, maintain the intestinal lining, and reduce TNF-related cell death. While current TNF-alpha inhibitors effectively treat inflammatory bowel diseases, they come with serious risks, such as higher infection rates. LL-37-based treatments could reduce reliance on these drugs and improve patient outcomes [13].
Research on cancer shows mixed results, but it may benefit intestinal and gastric cancers, including oral squamous cell carcinoma linked to smoking. Its effects are linked to a vitamin D-dependent pathway, which could explain the reduced risk of GI cancer associated with vitamin D intake. Vitamin D may enhance the anti-cancer activity of tumor-associated macrophages through LL-37 [14].
Growth of Blood Vessels: The cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide stimulates prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production in endothelial cells. PGE2, linked to inflammatory pain and blood vessel growth, has effects that vary by location. In endothelial cells, it promotes angiogenesis, which can be helpful or harmful depending on the context.
Regulating angiogenesis is crucial in conditions like cancer, heart disease, stroke recovery, and wound healing. The peptide provides a way to study angiogenesis and could help develop treatments—boosting blood vessel growth when needed (e.g. in heart disease) or blocking it when harmful (e.g. in cancer) [15].
Buy LL-37 CAP-18 Peptide Vial with 99% purity for research online today! Available as lyophilized powder in 5 mg vials.
Before use the vial needs to be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water which available in 10 ml and 30 ml from Direct Peptides .
Buy LL-37 Thymosin Alpha-1 Nasal Stack
Buy LL-37 Thymosin Alpha-1 Nasal Stack , it includes either two 15 ml spray bottles or two 30 ml spray bottles, offering a 10% discount compared to buying them separately.
This combination supports immune modulation and combines the benefits of LL-37 and Thymosin Alpha-1 for enhanced antimicrobial and immunoregulatory effects, all in a convenient nasal spray format.
Buy LL-37 CAP-18 Pre-Mixed 5mg Pen
Buy LL-37 CAP-18 pre-mixed 5mg pen a simple, ready-to-use option for administering the peptide. It provides accurate dosing, sterility, and convenience by removing the need for manual mixing. It’s ideal for in vivo laboratory research use, supporting immune function, and utilizing LL-37’s antimicrobial properties.
Pre-Mixed Cartridge Kits include a cartridge (pre-mixed with your selected peptide and Bacteriostatic Water), a pen, a carry case, and 3 needle tips. Single Cartridges (available in packs of 1, 2, or 3) include the pre-mixed cartridge and 3 needle tips but do not come with the full kit. Save 10% when you buy 3 cartridges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about LL-37 (CAP-18)
What is LL-37?
Also known as CAP-18, it is a human antimicrobial peptide that plays a crucial role in the immune system. It helps defend against infections by killing bacteria, viruses, and fungi, while also modulating the immune response to maintain balance and prevent excessive inflammation.
How does LL-37 work?
It works by disrupting the membranes of harmful microorganisms, effectively neutralising them. It also interacts with immune cells to promote the release of chemical signals like cytokines and chemokines, which help coordinate the immune response and support infection clearance.
What are the potential therapeutic uses of LL-37?
It has shown potential in a variety of therapeutic applications, including the treatment of chronic infections, wound healing, and inflammatory diseases. Its ability to modulate the immune response and enhance tissue repair makes it a promising candidate for clinical developments.
Summary of Research Applications
- Antimicrobial effects
- Improves immune system
- Accelerates wound healling
- Helps repair tissues
- Reduces inflammation
- Provides protection for lungs
- Promotes intestinal health
- Effects of angiogenesis
LL-37 (CAP-18) Peptide Quality Assured
Buy LL-37 CAP-18 peptides with 99% purity from Direct Peptides, designed to meet strict research standards. Trusted for safety and reliability, our products help researchers achieve accurate results with confidence.
These peptides are key in immune system research, providing insights into immunity, antimicrobial activity, inflammation, and therapeutic potential. Their versatility makes them valuable for immunology and microbiology studies. Buy LL-37 CAP-18 peptides from Direct Peptides to support your research.
References For Further Reading
[1] Alejandro Moreno-Angarita, Cristian C. Aragón, and Gabriel J. Tobón (2020) Cathelicidin LL-37: A new important molecule in the pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus – Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, Volume 3, 2020, 100029.
[2] J Michelle Kahlenberg and Mariana J Kaplan (2013) Little peptide, big effects: the role of LL-37 in inflammation and autoimmune disease – Journal of Immunology, 2013 Nov 15, Volume 191 (Issue 10), Pages 4895-901.
[3] D Kienhöfer, J Hahn, I Schubert, C Reinwald, et al (2014) No evidence of pathogenic involvement of cathelicidins in patient cohorts and mouse models of lupus and arthritis – PLoS One, 2014 Dec 23, Volume 9 (Issue 12), Page e115474.
[4] Leola N Y Chow, Ka-Yee Grace Choi, Hadeesha Piyadasa, et al (2014) Human cathelicidin LL-37-derived peptide IG-19 confers protection in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis – Molecular Immunology, 2014 Feb, Volume 57 (Issue 2), Pages 86-92.
[5] Wenhua Zhu, Liesu Meng, Congshan Jiang, Xiaojing He, et al (2011) Arthritis is associated with T-cell-induced upregulation of Toll-like receptor 3 on synovial fibroblasts – Arthritis Research & Therapy, 2011 Jun 27, Volume 13 (Issue 3), Page R103.
[6] Peck Y Ong, Takaaki Ohtake, Corinne Brandt, Ian Strickland, et al (2002) Endogenous antimicrobial peptides and skin infections in atopic dermatitis – The New England Journal of Medicine, 2002 Oct 10, Volume 347 (Issue 15), Pages 1151-60.
[7] Cristina D Ciornei, Thorgerdur Sigurdardóttir, Artur Schmidtchen, and Mikael Bodelsson (2005) Antimicrobial and chemoattractant activity, lipopolysaccharide neutralization, cytotoxicity, and inhibition by serum of analogs of human cathelicidin LL-37 – Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2005 Jul, Volume 49 (Issue 7), Pages 2845-50.
[8] Mehmet Demirci, Akin Yigin, and Cemil Demir (2022) Efficacy of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 against biofilm forming Staphylococcus aureus strains obtained from chronic wound infections – Microbial Pathogenesis, Volume 162, January 2022, 105368.
[9] Quanzhen Wang, Wei Wen, Lei Zhou, Fen Liu, et al (2024) LL-37 improves sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing pyroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells – International Immunopharmacology, Volume 129, 10 March 2024, 111580.
[10] Yuan-Yuan Jiang, Wei Xiao, Mao-Xiang Zhu, et al (2012) The effect of human antibacterial peptide LL-37 in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease -Respiratory Medicine, Volume 106, Issue 12, December 2012, Pages 1680-1689.
[11] Aaron Scott, Sinéad Weldon, Paul J Buchanan, Bettina Schock, et al (2011) Evaluation of the ability of LL-37 to neutralise LPS in vitro and ex vivo – PLoS One, 2011, Volume 6 (Issue 10) Page e26525.
[12] Jan-Michel Otte, Anna-Elisabeth Zdebik, Stephan Brand, et al (2009) Effects of the cathelicidin LL-37 on intestinal epithelial barrier integrity – Regulatory Peptides, Volume 156, Issues 1–3, 7 August 2009, Pages 104-117.
[13] Jan-Michel Otte, Ilka Werner, Stephan Brand, et al (2008) Human beta defensin 2 promotes intestinal wound healing in vitro – Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2008 Aug 15, Volume 104 (Issue 6), Pages 2286-97.
[14] Anand K. Keshri, Suraj S. Rawat, Anubha Chaudhary, et al (2025) LL-37, the master antimicrobial peptide, its multifaceted role from combating infections to cancer immunity – International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, Volume 65, Issue 1, January 2025, 107398.
[15] M Dolores Salvado, Antonio Di Gennaro, Lennart Lindbom, et al (2013) Cathelicidin LL-37 induces angiogenesis via PGE2-EP3 signaling in endothelial cells, in vivo inhibition by aspirin – Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 2013 Aug, Volume 33 (Issue 8), Pages 1965-72.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Direct Peptides website: https://direct-peptides.com is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Related Posts

Peptides For Immune System
This blog explores the potential of peptides in regulating the immune system. It highlights how peptides like Thymosin Alpha-1, TB500, and BPC-157 enhance immune responses, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair. While primarily for research, these peptides show promise in improving immune health and addressing immune-related conditions through targeted therapies.

What Are The Best Peptide Stacks?
This blog delves into the fascinating world of peptide stacks synergistic combinations of peptides designed to amplify their effects in scientific research. It explores their roles in muscle development, metabolic studies, cognitive enhancement, and immune function. Highlighting their transformative potential, the blog emphasizes their use strictly for research purposes, not human application.
KPV Peptide For The Gut: A Breakthrough In Digestive Health
This blog explores the potential of KPV Peptide in promoting gut health. It delves into its anti inflammatory, antimicrobial, and gut barrier enhancing properties, highlighting its role in reducing inflammation, repairing intestinal damage, and supporting microbiome balance. The article also examines its synergy with other peptides like BPC-157 for enhanced gut healing.

